Two Pointers - Sort Colors
All diagrams presented herein are original creations, meticulously designed to enhance comprehension and recall. Crafting these aids required considerable effort, and I kindly request attribution if this content is reused elsewhere.
Difficulty : Easy
Three Pointers , Partition of Array
Problem
Given an array nums with n objects colored red, white, or blue, sort them in-place so that objects of the same color are adjacent, with the colors in the order red, white, and blue.
We will use the integers 0, 1, and 2 to represent the color red, white, and blue, respectively.
- Input :
[2,0,2,1,1,0] - Output :
[0,0,1,1,2,2]
Solution
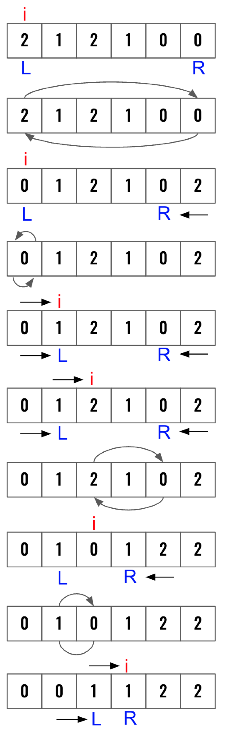
- High Level Idea: Move the
0’s to the left and2’s to the right.1will be automatically placed in the middle. - Use an index pointer i to traverse the array.
- Increment left and i pointer only when swapping 0s.
- Only decrement right pointer (don’t increment
i) when swapping 2s. Left pointer can only point to 1, however right pointer can point to both 0 or 1. This is why index pointer i can not be moved unless validated with left pointer in the next iteration.
Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
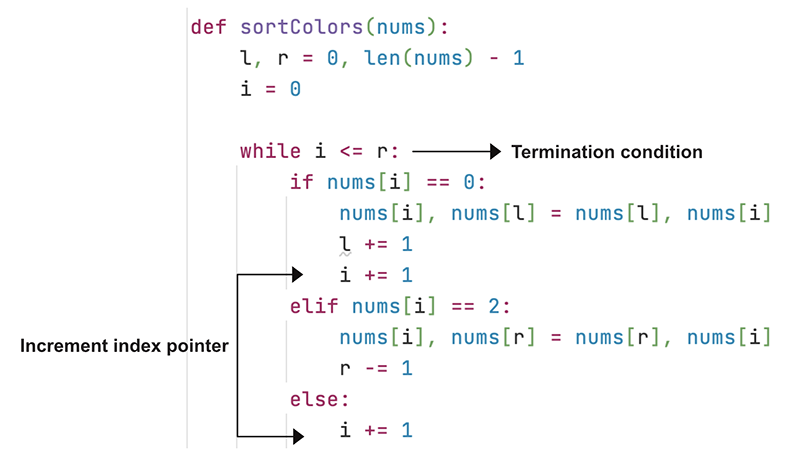
def sort_colors(nums):
# Initialize left and right pointers
l, r = 0, len(nums)-1
# Initialize index pointer
i = 0
# Break when both index pointer
# and right pointer are pointing
# to the same location
while i <= r:
# First swap logic
if nums[i] == 0:
# Swap with content from left pointer
nums[i], nums[l] = nums[l], nums[i]
# Increament both as left & index pointer
i += 1
l += 1
elif nums[i] == 2:
# Swap with content from right pointer
nums[i], nums[r] = nums[r], nums[i]
# Only decrement right as index might point to 0.
# In that case need to swap index with left pointer again.
r -= 1
else:
# no need to swap and index ptr
# is already pointing to 1
i += 1
return nums
print(sort_colors([2, 0, 2, 1, 1, 0]))
1
[0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2]
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.